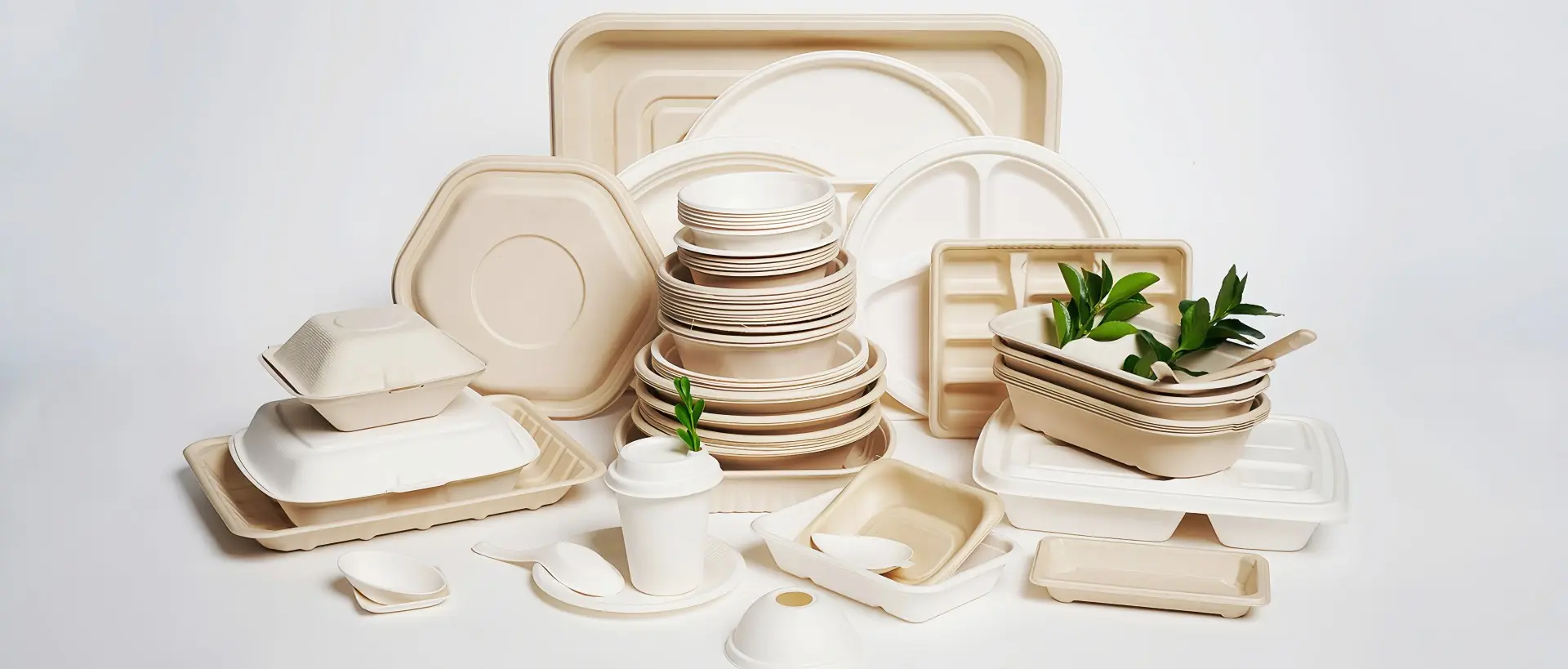
01
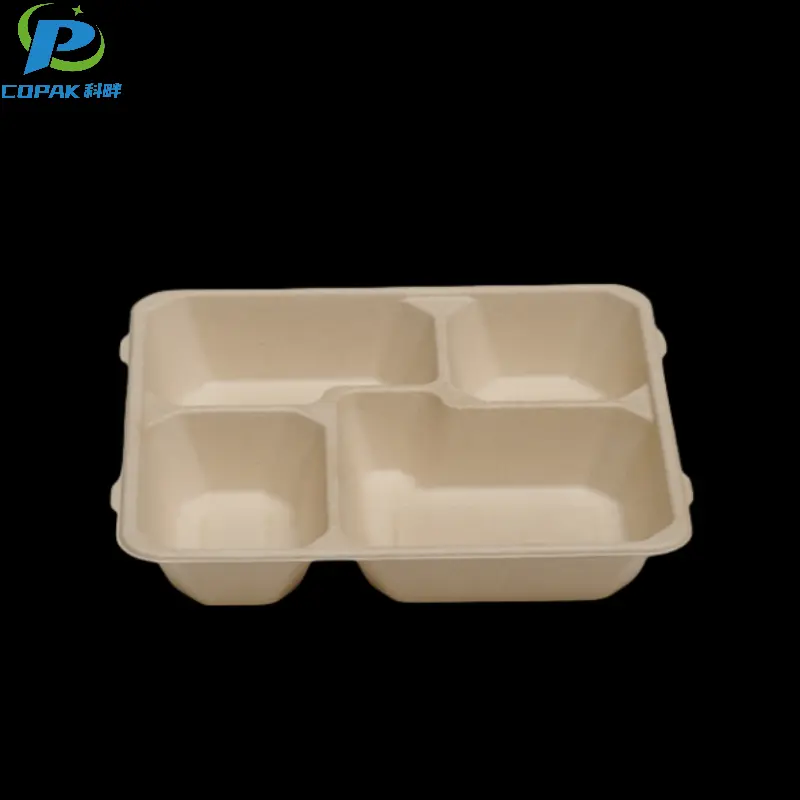
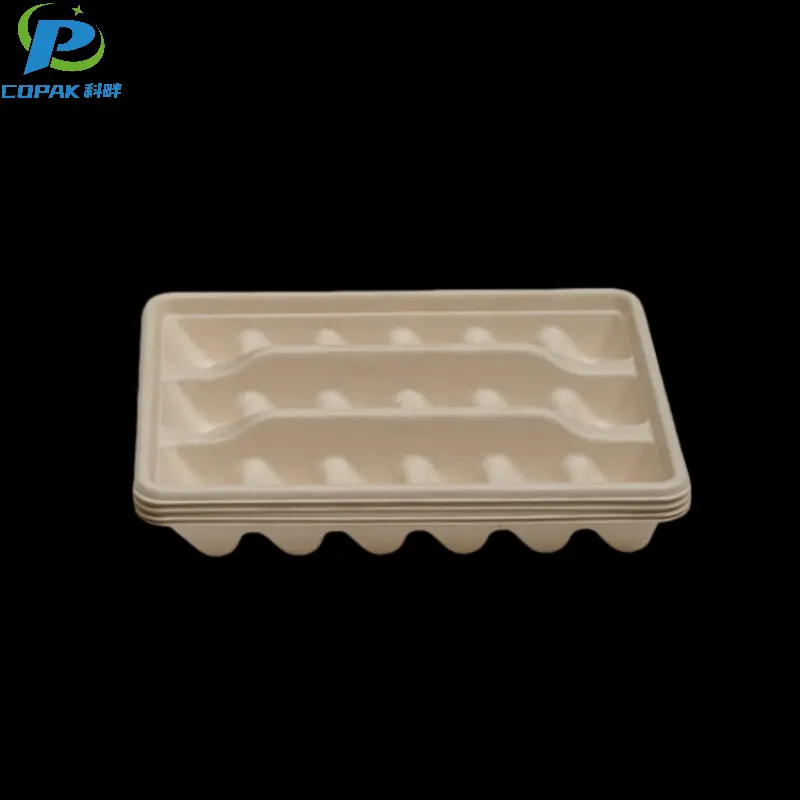
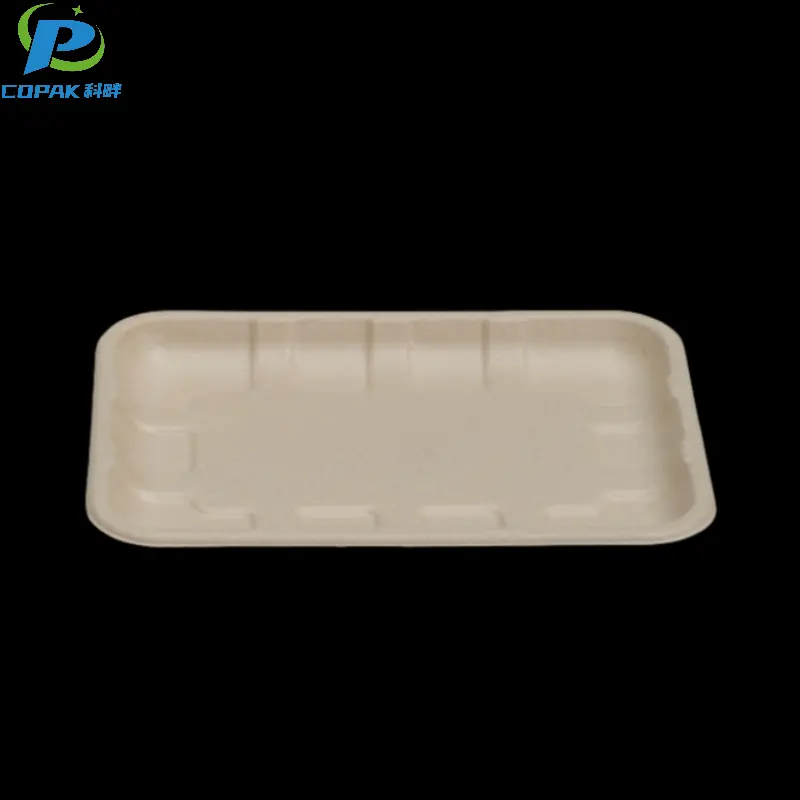
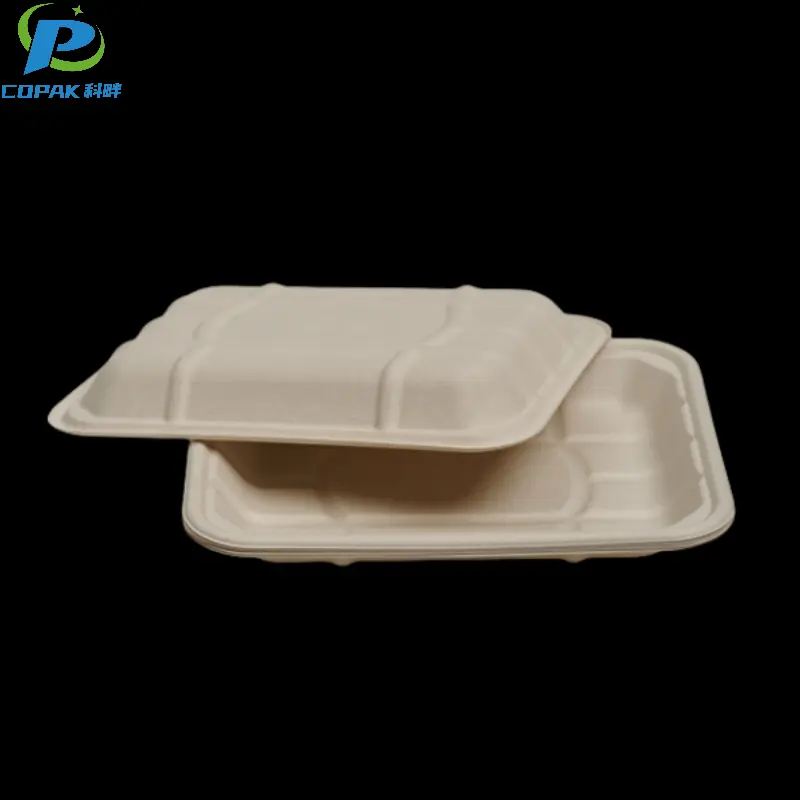
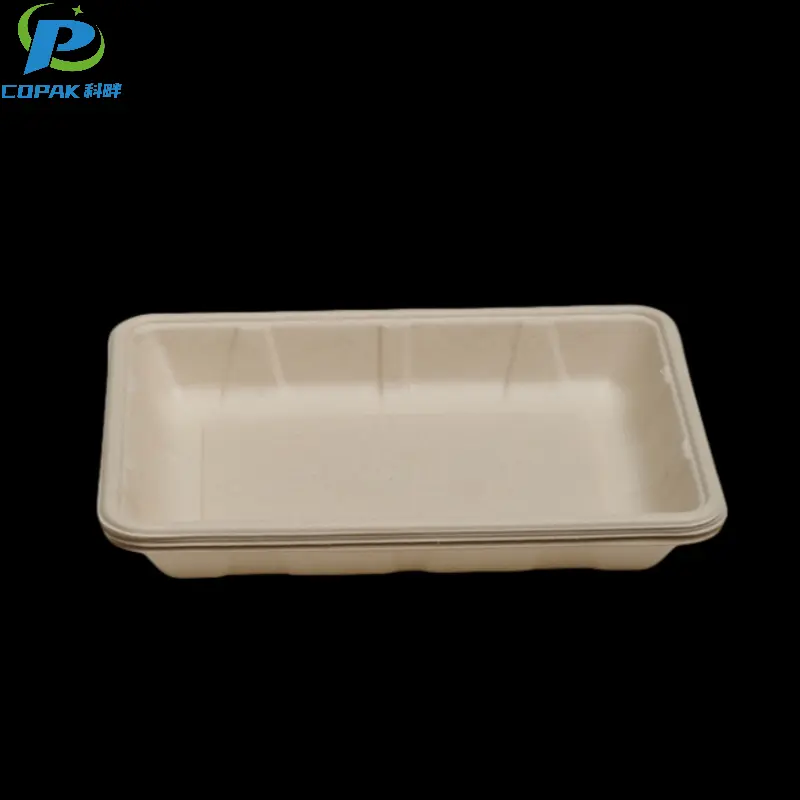
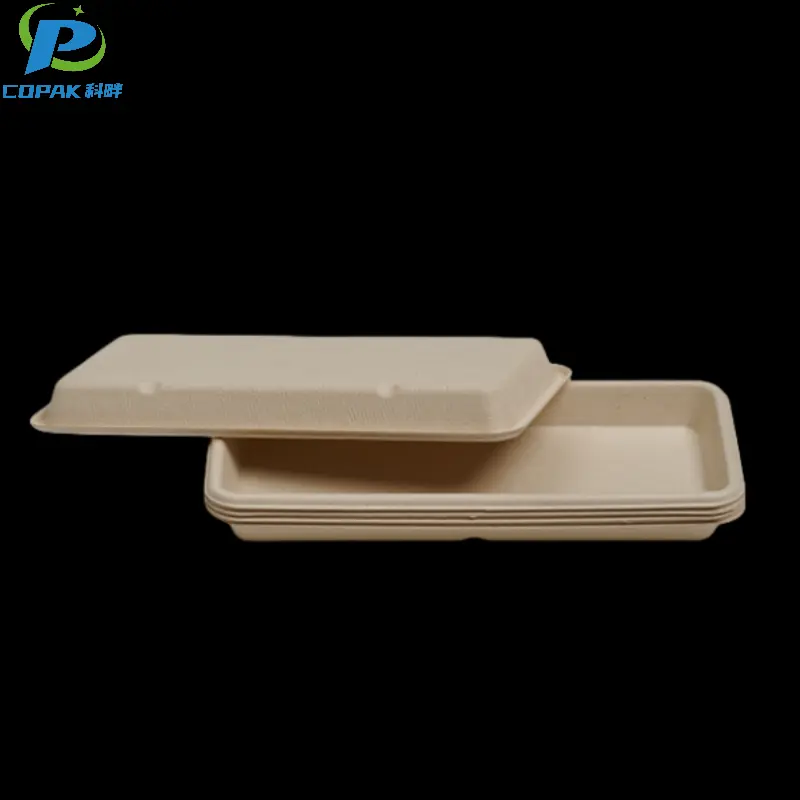
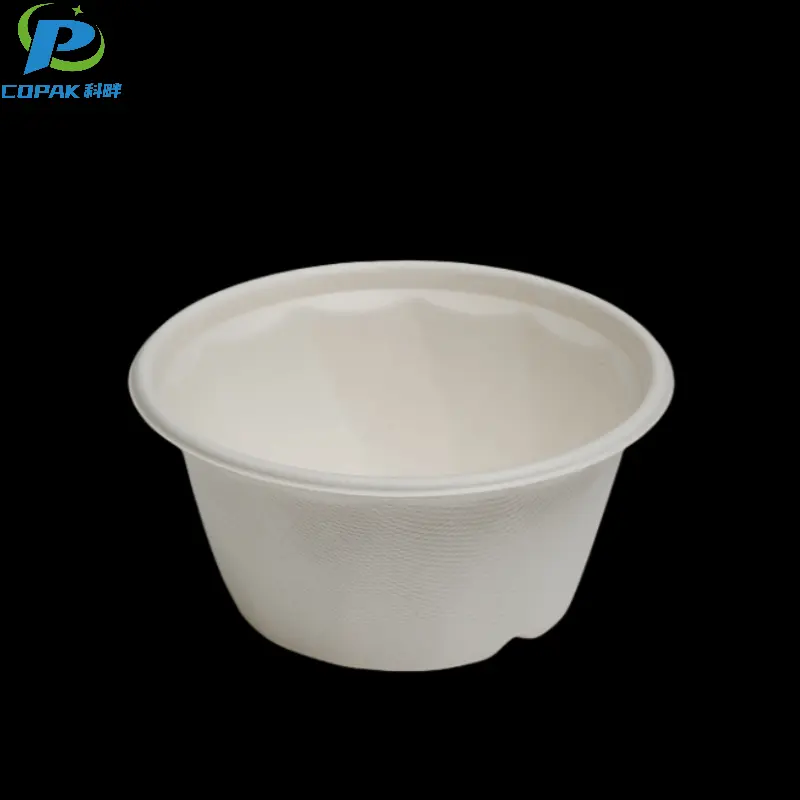
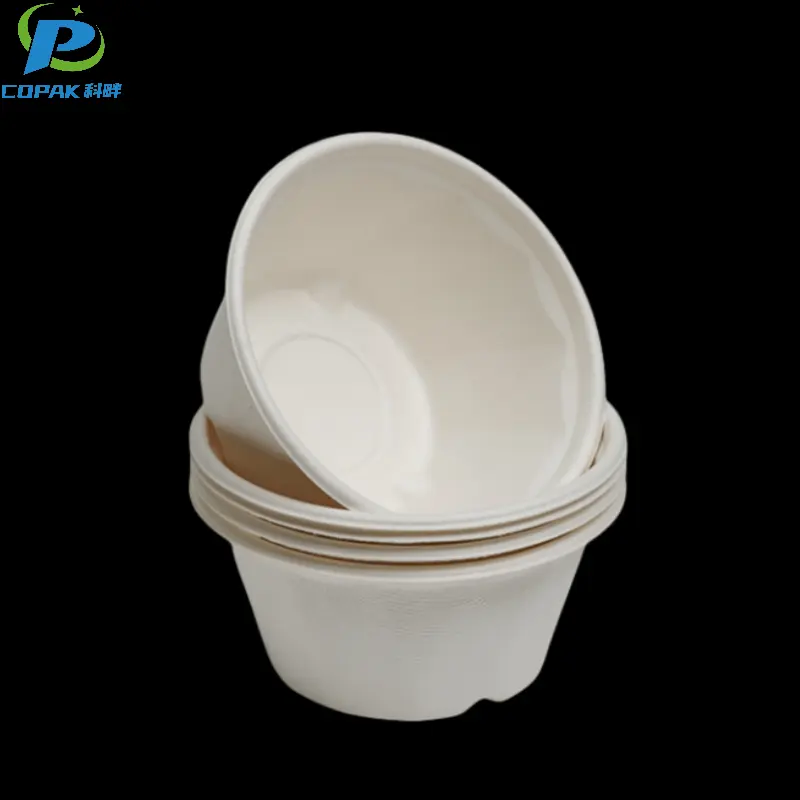
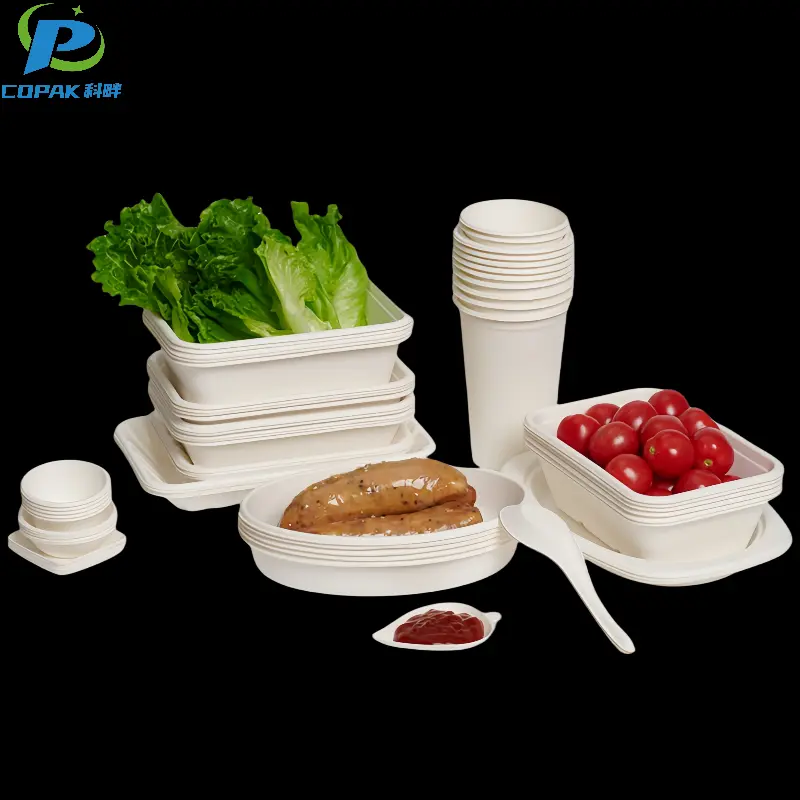
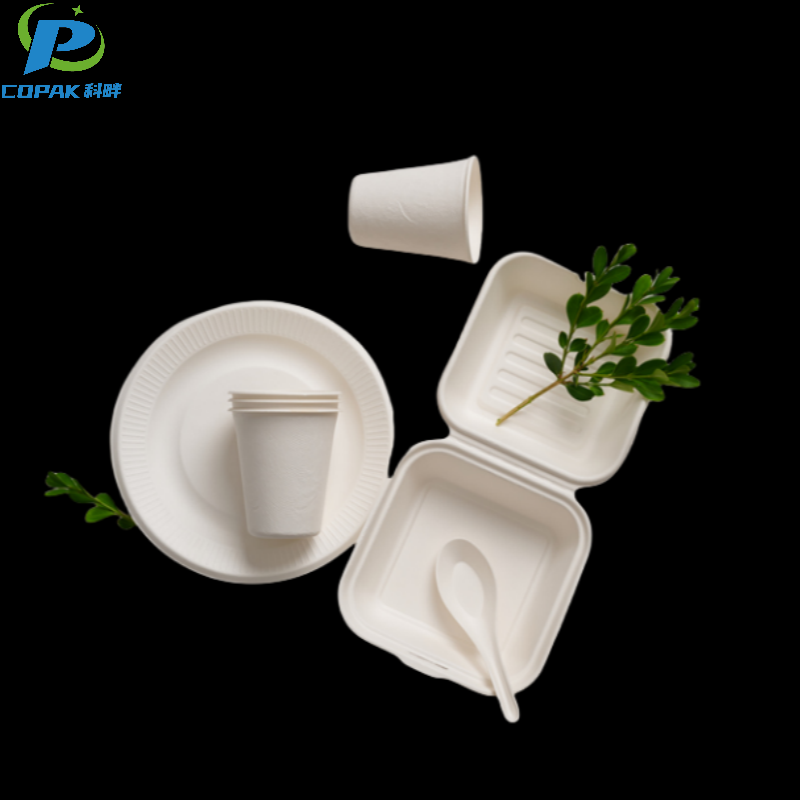
16oz sustainable sugarcane bagasse soup cup
description1
description2
Specification
|
Size (mm) |
Ø125*60 |
|
Weight (g) |
12 |
|
Carton Size (cm) |
64*29.5*26.5 |
|
Packing (pcs) |
50*10 |
|
Raw Material |
Sugarcane Bagasse Pulp |
|
Product Service |
Free sample with postage at your own expense |

Bagasse cups, like other products made from bagasse, are biodegradable and can compost in nature. The time it takes for a bagasse cup to decompose can vary based on several factors, including environmental conditions such as temperature, moisture, and the presence of microorganisms.
General Composting Timeline:
Under Ideal Conditions: In a well-maintained composting environment, bagasse products can break down in about 30 to 90 days.
In Natural Settings: If left in a natural environment (like a backyard or garden), the decomposition process may take longer, typically ranging from 3 to 6 months or more, depending on the conditions.
Factors Affecting Decomposition:
Moisture: Adequate moisture levels can speed up the composting process.
Temperature: Warmer temperatures generally promote faster decomposition.
Microbial Activity: The presence of microorganisms and other decomposers is crucial for breaking down organic materials.
Oxygen Levels: Aerobic conditions (with oxygen) facilitate faster composting compared to anaerobic conditions (without oxygen).
To ensure optimal composting, it’s best to place bagasse cups in a compost bin or pile where conditions can be controlled.
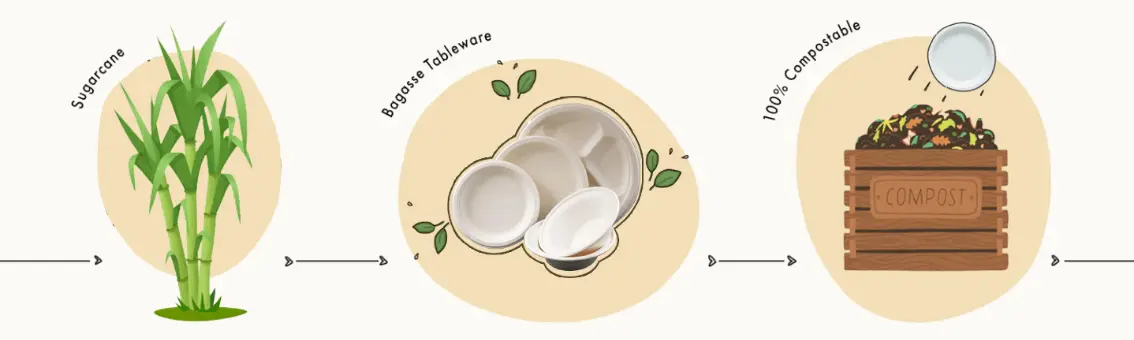

Bagasse cups are generally considered an eco-friendly alternative
Bagasse cups are generally considered an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic or Styrofoam cups, and they have a lower environmental impact. However, like any product, their production, use, and disposal can have some environmental implications. Here’s a breakdown:
Pollution Considerations:
Production Process:
The manufacturing of bagasse cups involves processing sugarcane waste, which is more sustainable than producing plastic. However, if the production process uses excessive energy or harmful chemicals, it could contribute to pollution.
Biodegradability:
Bagasse cups are biodegradable and compostable, meaning they can break down naturally in the environment. When disposed of properly in a composting facility, they do not contribute to long-term pollution. However, if they end up in a landfill, the decomposition process can be slower due to anaerobic conditions, potentially leading to methane emissions.
Microplastics:
Unlike plastic cups, bagasse cups do not break down into microplastics, which are a significant environmental concern. This makes them a better option in terms of pollution.
Chemical Additives:
Some bagasse products may contain chemical coatings or additives for water resistance or durability. If these chemicals are not environmentally friendly, they could pose a pollution risk when the cups break down.
Conclusion:
Overall, bagasse cups are a more sustainable choice compared to conventional plastic cups, and they contribute less to pollution when managed properly. To minimize environmental impact, it’s essential to dispose of them in composting facilities rather than landfills whenever possible.

Production Process


















